- Sharon Rajendra Manmothe

- Dec 5, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Dec 8, 2025
Creating a Jenkins Pipeline can be done in two ways: directly in the Jenkins Web UI (good for testing) or using a Jenkinsfile from Source Control (Best Practice).
Here is the step-by-step guide to setting up your first Declarative Pipeline.
Phase 1: Create the Job in Jenkins
Login to your Jenkins Dashboard.
Click on New Item in the top-left menu.
Enter a name for your pipeline (e.g., My-First-Pipeline).
Select Pipeline from the list of project types.
Click OK at the bottom.
Phase 2: Configure the Pipeline Script
You will be redirected to the Configuration page. Scroll down to the section labeled Pipeline. Here you have two choices:
Direct Script
Find the Definition dropdown.
Select Pipeline script.
Copy and paste the following "Hello World" code into the text area:
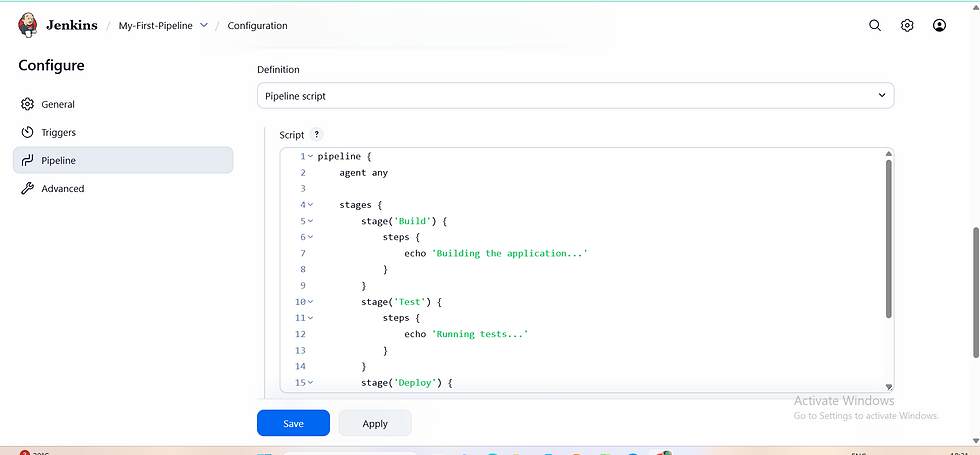
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Building the application...'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
echo 'Running tests...'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Deploying to production...'
}
}
}
}
Phase 3: Run the Pipeline
Click Save at the bottom of the page.
You will be taken to the Project Dashboard. Click Build Now in the left-hand menu.
Look at the Build History on the bottom left. You will see a flashing entry (e.g., #1).
Click on the build number (#1) and then click Console Output to see the logs.
Pipeline from SCM
Go to your Repository: Open your browser and navigate to Add a New File:
in your repository
Click the "Add file" button (or the "Create new file" button if the repo is empty).
Name the File: In the file name field, type the exact name:
Jenkinsfile
Paste the Content:
This script outlines the three core stages of Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Build, Test, and Deploy.
Groovy
pipeline {
// 1. Agent: Defines where the pipeline runs. 'any' means any available Jenkins agent/node.
agent any
// 2. Stages: Defines the sequence of work to be performed.
stages {
stage('Checkout Source Code') {
steps {
// This command tells Jenkins to pull the code from the Git repository
// that you configured in the job settings.
checkout scm
echo "Source code successfully checked out."
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo "Starting application build..."
// Replace the 'echo' below with your actual build command (e.g., sh 'npm install' or sh 'mvn package')
echo "Build completed successfully."
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
echo "Running unit and integration tests..."
// Replace the 'echo' below with your actual test command (e.g., sh 'npm test' or sh 'mvn test')
echo "All tests passed."
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo "Deploying application to environment..."
// Replace the 'echo' below with your deployment commands (e.g., sh 'docker push' or sh 'scp')
echo "Deployment finished."
}
}
}
// 3. Post: Actions to run after the pipeline completes, regardless of success or failure.
post {
always {
echo 'Pipeline job finished.'
}
failure {
echo 'The Pipeline FAILED! Review the console output immediately.'
}
success {
echo 'Pipeline successfully completed all stages.'
}
}
}
Commit the Change:
Scroll down to the bottom.
Add a short commit message (e.g., "Add initial Jenkinsfile").
Click the green "Commit new file" button.
Find the Definition dropdown.
Select Pipeline script from SCM.
SCM: Select Git.
Repository URL: Paste your GitHub/GitLab repo URL.
Credentials: Select your git credentials (if the repo is private).
Script Path: Ensure this says Jenkinsfile (this means Jenkins will look for a file with that exact name in the root of your repo).
Run the Pipeline
Click Save at the bottom of the page.
You will be taken to the Project Dashboard. Click Build Now in the left-hand menu.
Look at the Build History on the bottom left. You will see a flashing entry (e.g., #1).
Click on the build number (#1) and then click Console Output to see the logs.
How to Create a Jenkins Pipeline Locally and Build It from GitHub
1) Create empty repo on GitHub
Go to GitHub → New repository.
Name it e.g. jenkins-pipeline-demo.
Important: Do NOT add README, .gitignore or license (choose Create repository with an empty repo).
Copy the repo URL (HTTPS): https://github.com/YOURUSERNAME/jenkins-pipeline-demo.git
2) Clone the repo to local (VS Code terminal)
Open VS Code → open Terminal (`Ctrl+``) and run:
# choose a folder where you want the project
cd C:\path\to\projects
# clone the empty repo
git clone https://github.com/YOURUSERNAME/jenkins-pipeline-demo.git
cd jenkins-pipeline-demo
# open folder in VS Code
code .
If Git asks for credentials when cloning a private repo, use username + PAT, or use SSH cloning if you prefer.
3) Create the Jenkinsfile locally
In VS Code:
In Explorer → click New File → name it Jenkinsfile (no extension).
Paste this minimal pipeline:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello from Jenkinsfile in GitHub!'
}
}
}
}
Save the file.
4) Commit & push from VS Code (Terminal or Source Control)
Using terminal in VS Code:
git add Jenkinsfile
git commit -m "Add Jenkinsfile - initial pipeline"
git push origin main
Notes:
If main branch doesn’t exist locally, create it:git branch -M mainthen push.
If git asks for username/password for HTTPS, use your GitHub username and a Personal Access Token (PAT) as password (recommended). Or set up SSH keys.
VS Code GUI alternative: Use Source Control tab → Stage → Commit → Push.
5) Run Jenkins in Docker (make sure container has git)
You said you run Jenkins in Docker. Use this recommended command to start Jenkins with persistent volume and port 8080:
docker run -d --name jenkins \
-p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
-v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home \
jenkins/jenkins:lts
6) Create Jenkins Pipeline job pointing to GitHub
Jenkins → New Item → Enter name (e.g., My-GitHub-Pipeline) → Pipeline → OK
In job configuration → Pipeline section:
Definition: Pipeline script from SCM
SCM: Git
Repository URL: https://github.com/YOURUSERNAME/jenkins-pipeline-demo.git
Credentials: choose the credential you added (or none if repo is public)
Branch: */main
Script Path: Jenkinsfile
Save.
7) Build / Test
Click Build Now.Go to the Build → Console Output and you should see:
Hello from Jenkinsfile in GitHub!